Step-by-step Guides to Implement RecycleView
Simple RecycleView demo to create dynamic lists to efficiently display large sets of data for your Android app
Table of contents
- 1. Implement and create ViewModel to hold RecycleView ItemData
- 2. Implement RecycleView item.xml layout
- 3. Add RecycleView into MainFragment layout
- 4. ImplementItemViewHolder that extends RecycleView.ViewHolder
- 5. Implement ItemDiffCallback singleton object
- 6. Implement RecycleViewAdapter that extends ListAdapter
- 7. Create RecycleViewAdapter and assign it to RecycleView in onCreateView() fragment
- References
- See Also
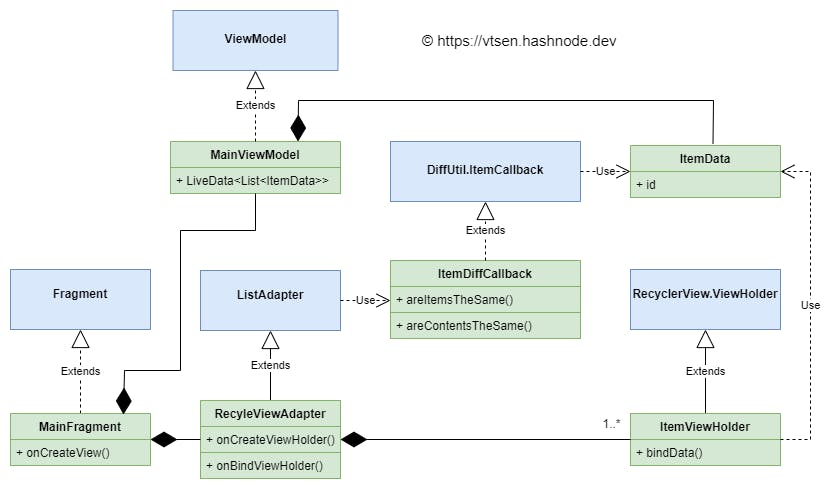
This is the Android RecycleView adapter architecture class diagram. I draw this because it helps me to understand the overall picture.
1. Implement and create ViewModel to hold RecycleView ItemData
This is just an example of recycle view ItemData. For simplicity, it just holds one data, which is the id.
data class ItemData (val id : Int)
mockItems() is used to create a fake data. In practice, the data could be coming from repository either through remote and local data source.
class MainViewModel : ViewModel() {
private val _items = MutableLiveData<List<ItemData>>()
val items: LiveData<List<ItemData>>
get() = _items
init {
mockItems()
}
private fun mockItems() {
val itemDataList = mutableListOf<ItemData>()
for(count in 1..100) {
val data = ItemData(id = count)
itemDataList.add(data)
}
_items.postValue(itemDataList)
}
}
In MainFragment, create the ViewModel. See my previous post - Recommended Ways To Create ViewModel
private val viewModel: MainViewModel by viewModels()
2. Implement RecycleView item.xml layout
item.xml represents a single element in the RecycleView.
Before updating the layout, you need to enable the data binding in your app build.gradle.
buildFeatures {
dataBinding true
}
Add data variable into the item.xml, add TextView and assign the itemData.Id to the android:text attribute.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<data>
<variable
name="itemData"
type="com.example.android.recycleviewdemo.ui.main.ItemData" />
</data>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView android:id="@+id/itemId"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@{Integer.toString(itemData.id)}"
android:textAppearance="@style/TextAppearance.AppCompat.Large"
android:textSize="34sp"
android:textStyle="bold"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
tools:text="1" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
</layout>
3. Add RecycleView into MainFragment layout
Add viewModel data variable, add RecycleView (uses LinearLayoutManager).
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<data>
<variable
name="viewModel"
type="com.example.android.recycleviewdemo.ui.main.MainViewModel" />
</data>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
android:id="@+id/main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".ui.main.MainFragment">
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/recycler_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
app:layoutManager="androidx.recyclerview.widget.LinearLayoutManager"
tools:listitem="@layout/item"/>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
</layout>
4. ImplementItemViewHolder that extends RecycleView.ViewHolder
Implement the bindData() function bind the itemData into item layout view.
class ItemViewHolder(
private val binding: ItemBinding
) : RecyclerView.ViewHolder(binding.root) {
private lateinit var _itemData: ItemData
fun bindData(itemData: ItemData) {
_itemData = itemData
binding.itemData = _itemData
binding.executePendingBindings()
}
}
5. Implement ItemDiffCallback singleton object
This is required in the next step to create the RecycleViewAdapter
object ItemDiffCallback : DiffUtil.ItemCallback<ItemData>() {
override fun areItemsTheSame(oldItem: ItemData, newItem: ItemData): Boolean {
return oldItem.id == newItem.id
}
override fun areContentsTheSame(oldItem: ItemData, newItem: ItemData): Boolean {
return (oldItem == newItem)
}
}
6. Implement RecycleViewAdapter that extends ListAdapter
Extents ListAdapter<ItemData, ItemViewHolder> and passing in the ItemDiffCallback, implement onCreateViewHolder() and onBindViewHolder() functions.
class RecycleViewAdapter()
: ListAdapter<ItemData, ItemViewHolder> (ItemDiffCallback) {
override fun onCreateViewHolder(parent: ViewGroup, viewType: Int): ItemViewHolder {
val itemBinding = ItemBinding.inflate(
LayoutInflater.from(parent.context),
parent, false)
return ItemViewHolder(itemBinding)
}
override fun onBindViewHolder(holder: ItemViewHolder, position: Int) {
holder.bindData(getItem(position))
}
}
7. Create RecycleViewAdapter and assign it to RecycleView in onCreateView() fragment
You also need to observe the viewModel.item live data and call ListAdapter.submitList()
override fun onCreateView(
inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?
): View {
val binding = MainFragmentBinding.inflate(inflater)
val adapter = RecycleViewAdapter()
binding.recyclerView.adapter = adapter
viewModel.items.observe(viewLifecycleOwner, { items ->
adapter.submitList(items)
})
return binding.root
}
That's it! It is done!
References
- Source code used in this example: Simple RecycleView Demo
- For more sophisticated
RecycleViewexample, you can refer to my Malaysian Sydney Food App.